Introduction to Haryana
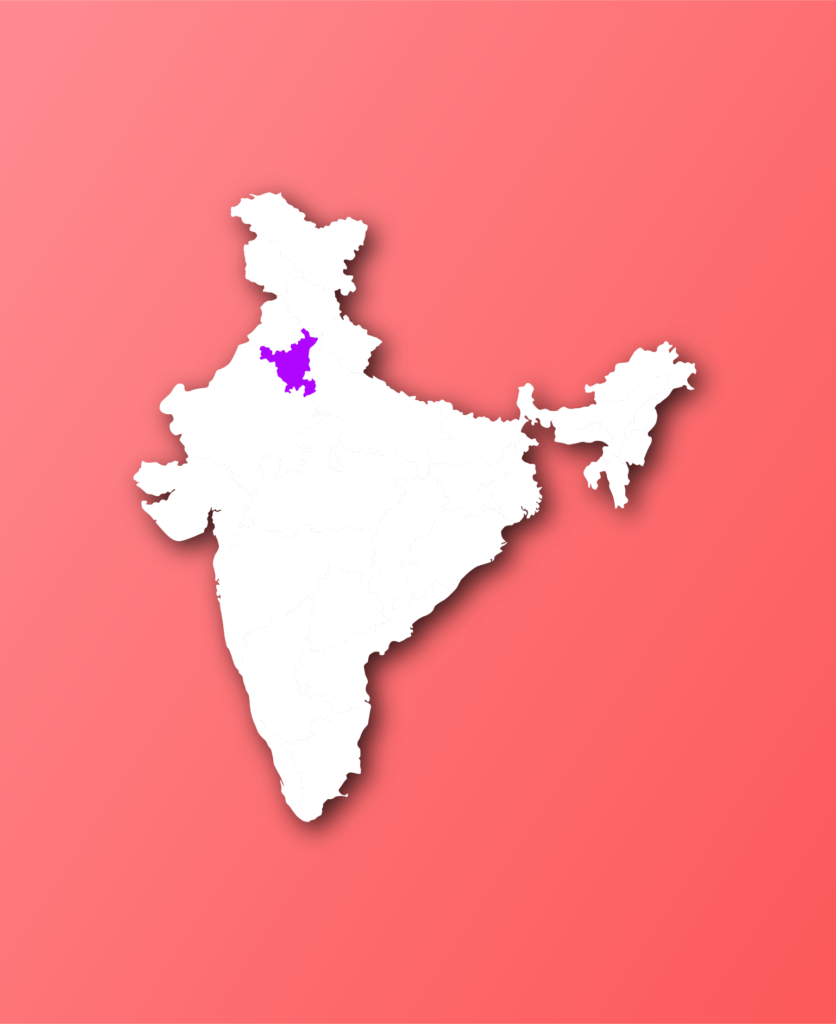
Haryana, located in the northern part of India, is a state rich in history and cultural heritage. Established on November 1, 1966, it was carved out of the former state of Punjab to create a distinct identity for its predominantly Hindi-speaking population.
Geography and Climate
Situated on the fertile plains of the river Indus, Haryana boasts a diverse landscape comprising agricultural fields, forests, and urban centers. The state experiences extreme temperatures, with scorching summers and chilly winters, making it essential for visitors to plan their trips accordingly.
Cultural Heritage

Haryana is renowned for its vibrant cultural tapestry, woven from the threads of various communities residing in the region. From folk dances like Ghoomar and Phag to festivals like Teej and Holi, the state pulsates with celebratory fervor year-round, showcasing its rich traditions.
Economic Landscape
The state’s economy relies mainly on agriculture, manufacturing, and services industries. This state is a leading producer of wheat, rice, and sugarcane, contributing significantly to India’s food basket. Additionally, it houses several industrial hubs, including Gurgaon and Faridabad, which are home to numerous multinational corporations.
Education and Literacy
Haryana places a strong emphasis on education, boasting a network of prestigious educational institutions and research centers. The state has made commendable progress in improving literacy rates, with concerted efforts to ensure access to quality education for all sections of society.
Government and Politics
Administratively, Haryana is divided into districts, each governed by a district magistrate. The state has a robust political landscape, with multiple parties vying for power in regular elections. The government is committed to ensuring effective governance and development across all sectors.
Tourism
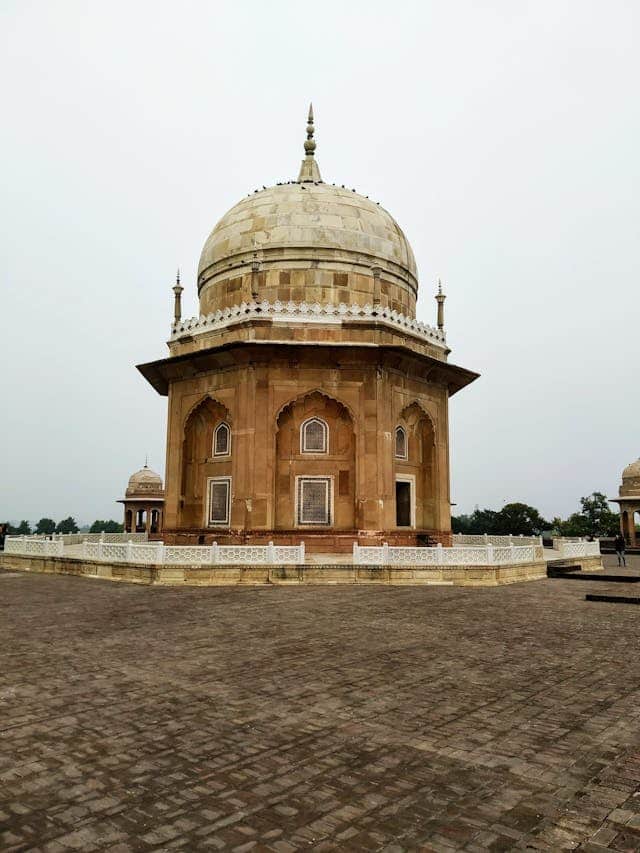

Haryana offers a plethora of tourist attractions, ranging from historical monuments like the Kurukshetra battlefield to scenic locales like the Sultanpur Bird Sanctuary. Visitors can immerse themselves in the state’s rich cultural heritage while exploring its diverse landscapes.
Infrastructure Development
In recent years, Haryana has witnessed significant infrastructure development, with a focus on enhancing transportation networks and urban amenities. Projects like the Delhi-Mumbai Industrial Corridor and the Kundli-Manesar-Palwal Expressway have propelled the state’s economic growth and connectivity.
Agriculture
Agriculture forms the backbone of Haryana’s economy, with the majority of its population engaged in farming activities. The state is known for its adoption of modern farming techniques and high-yield crop varieties, ensuring food security and agricultural sustainability.
Social Welfare Programs
The government of Haryana has implemented various social welfare programs aimed at uplifting marginalized communities and providing them with access to basic amenities and opportunities for growth. Initiatives like Beti Bachao Beti Padhao and Antyodaya Saral are testament to the state’s commitment to social equity.
Healthcare System
Haryana boasts a robust healthcare infrastructure, with a network of hospitals, clinics, and primary health centers catering to the medical needs of its residents. The state government has launched several public health initiatives to address prevalent diseases and improve healthcare delivery.
Sports and Recreation
Sports play a vital role in the cultural fabric of Haryana, with the state producing numerous athletes who have excelled on national and international platforms. From wrestling to kabaddi, It has a rich sporting heritage, with ample opportunities for recreation and physical fitness.
Environmental Conservation
Recognizing the importance of environmental conservation, Haryana has taken proactive measures to protect its natural resources and promote sustainable development. Afforestation drives, water conservation projects, and pollution control measures are integral to the state’s environmental agenda.
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its many strengths, Haryana faces challenges such as urbanization, water scarcity, and environmental degradation. However, with concerted efforts and strategic planning, the state holds immense potential for future growth and development, leveraging its demographic dividend and economic opportunities.
Conclusion
Haryana, with its rich cultural heritage, robust economy, and proactive governance, stands as a shining example of progress and prosperity in northern India. As it continues to navigate the complexities of modernity while staying true to its roots, the state remains poised for a promising future filled with opportunities for all its residents.
Picture credits: https://www.pexels.com/ ; https://pixabay.com/
Like this post?
Give a glance to our other posts too : https://indyviews.in/blogsy/